
Sign up to save your podcasts
Or




Researchers have developed a skin-permeable polymer that can deliver insulin into the body, which they say could one day offer an alternative to injections for diabetes management. The skin’s structure presents a formidable barrier to the delivery of large drugs but in this work a team show that their polymer can penetrate though the different layers without causing damage. Insulin attached to this polymer was able to reduce blood glucose levels in animal models for diabetes at a comparable speed to injected insulin. While further research is required on the long-term safety of this strategy, the team hope it could offer a way to non-invasively deliver other large-molecule drugs into the body.
Research Article: Wei et al.
How extreme drought may be humanity’s biggest challenge after a huge volcanic eruption — plus, turning a bacterium into a factory for a colour-changing pigment
Research Highlight: Volcano mega-eruptions lead to parched times
Research Highlight: Dye or die: bacterium forced to make pigment to stay alive
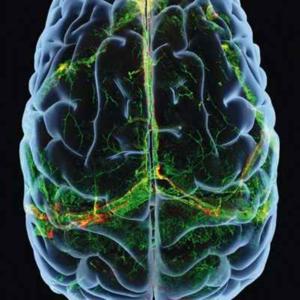
The human brain responds in a similar way to both familiar and unfamiliar languages, but there are some key differences, according to new research — a finding that may explain why learning a language can be difficult. A study looking involving 34 people showed that listening to an unfamiliar language triggers similar neural activity to listening to their native tongue. The finding implies that human speech triggers a common reaction in the brain regardless of understanding. However, there were subtle differences when listening to a known language that may help explain how people actually understand words.
Research Article: Bhaya-Grossman et al.
Neuron: Zhang et al
Sounds used under CC BY 4.0
Signs that greenhouse-gas emissions may peak around 2030 — plus, evidence of dog breeding by ancient humans.
Nature: Global greenhouse-gas emissions are still rising: when will they peak?
Nature: How ancient humans bred and traded the first domestic dogs
Subscribe to Nature Briefing, an unmissable daily round-up of science news, opinion and analysis free in your inbox every weekday.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.
 View all episodes
View all episodes


 By Springer Nature Limited
By Springer Nature Limited




4.5
721721 ratings

Researchers have developed a skin-permeable polymer that can deliver insulin into the body, which they say could one day offer an alternative to injections for diabetes management. The skin’s structure presents a formidable barrier to the delivery of large drugs but in this work a team show that their polymer can penetrate though the different layers without causing damage. Insulin attached to this polymer was able to reduce blood glucose levels in animal models for diabetes at a comparable speed to injected insulin. While further research is required on the long-term safety of this strategy, the team hope it could offer a way to non-invasively deliver other large-molecule drugs into the body.
Research Article: Wei et al.
How extreme drought may be humanity’s biggest challenge after a huge volcanic eruption — plus, turning a bacterium into a factory for a colour-changing pigment
Research Highlight: Volcano mega-eruptions lead to parched times
Research Highlight: Dye or die: bacterium forced to make pigment to stay alive
The human brain responds in a similar way to both familiar and unfamiliar languages, but there are some key differences, according to new research — a finding that may explain why learning a language can be difficult. A study looking involving 34 people showed that listening to an unfamiliar language triggers similar neural activity to listening to their native tongue. The finding implies that human speech triggers a common reaction in the brain regardless of understanding. However, there were subtle differences when listening to a known language that may help explain how people actually understand words.
Research Article: Bhaya-Grossman et al.
Neuron: Zhang et al
Sounds used under CC BY 4.0
Signs that greenhouse-gas emissions may peak around 2030 — plus, evidence of dog breeding by ancient humans.
Nature: Global greenhouse-gas emissions are still rising: when will they peak?
Nature: How ancient humans bred and traded the first domestic dogs
Subscribe to Nature Briefing, an unmissable daily round-up of science news, opinion and analysis free in your inbox every weekday.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.

876 Listeners

1,391 Listeners

603 Listeners

943 Listeners

94 Listeners

0 Listeners
15 Listeners

5 Listeners

551 Listeners

963 Listeners

413 Listeners

427 Listeners

817 Listeners

6,444 Listeners

228 Listeners

363 Listeners

475 Listeners

110 Listeners