
Sign up to save your podcasts
Or




A newly-developed method that can rapidly identify the type of bacteria causing a blood-infection, and the correct antibiotics to treat it, could save clinicians time, and patient lives. Blood infections are serious, and can lead to the life-threatening condition sepsis, but conventional diagnostic methods can take days to identify the causes. This new method does away with some of the time-consuming steps, and the researchers behind it say that if it can be fully automated, it could provide results in less than a day.
Research Article: Kim et al.
The discovery of a connection between three star-forming interstellar clouds could help explain how these giant structures form, and evidence of the largest accidental methane leak ever recorded.
Research Highlight: Found: the hidden link between star-forming molecular clouds
Research Highlight: Blowout! Satellites reveal one of the largest methane leaks on record
When artificial intelligences are fed data that has itself been AI-generated, these systems quickly begin to spout nonsense responses, according to new research. Typically, large language model (LLM) AI’s are trained on human-produced text found online. However, as an increasing amount of online content is AI-generated, a team wanted to know how these systems would cope. They trained an AI to produce Wikipedia-like entries, then trained new iterations on the model on the text produced by its predecessor. Quickly the outputs descended into gibberish, which highlights the dangers of the Internet becoming increasingly full of AI-generated text.
Research Article: Shumailov et al.
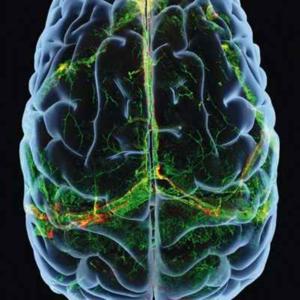
How psilocybin — the hallucinogenic compound found in magic mushrooms — resets communication between brain regions, and the surprise cancellation of a NASA Moon mission.
Nature News: Your brain on shrooms — how psilocybin resets neural networks
Nature News: NASA cancels $450-million mission to drill for ice on the Moon — surprising researchers
Subscribe to Nature Briefing, an unmissable daily round-up of science news, opinion and analysis free in your inbox every weekday.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.
 View all episodes
View all episodes


 By Springer Nature Limited
By Springer Nature Limited




4.5
716716 ratings

A newly-developed method that can rapidly identify the type of bacteria causing a blood-infection, and the correct antibiotics to treat it, could save clinicians time, and patient lives. Blood infections are serious, and can lead to the life-threatening condition sepsis, but conventional diagnostic methods can take days to identify the causes. This new method does away with some of the time-consuming steps, and the researchers behind it say that if it can be fully automated, it could provide results in less than a day.
Research Article: Kim et al.
The discovery of a connection between three star-forming interstellar clouds could help explain how these giant structures form, and evidence of the largest accidental methane leak ever recorded.
Research Highlight: Found: the hidden link between star-forming molecular clouds
Research Highlight: Blowout! Satellites reveal one of the largest methane leaks on record
When artificial intelligences are fed data that has itself been AI-generated, these systems quickly begin to spout nonsense responses, according to new research. Typically, large language model (LLM) AI’s are trained on human-produced text found online. However, as an increasing amount of online content is AI-generated, a team wanted to know how these systems would cope. They trained an AI to produce Wikipedia-like entries, then trained new iterations on the model on the text produced by its predecessor. Quickly the outputs descended into gibberish, which highlights the dangers of the Internet becoming increasingly full of AI-generated text.
Research Article: Shumailov et al.
How psilocybin — the hallucinogenic compound found in magic mushrooms — resets communication between brain regions, and the surprise cancellation of a NASA Moon mission.
Nature News: Your brain on shrooms — how psilocybin resets neural networks
Nature News: NASA cancels $450-million mission to drill for ice on the Moon — surprising researchers
Subscribe to Nature Briefing, an unmissable daily round-up of science news, opinion and analysis free in your inbox every weekday.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.

1,384 Listeners

615 Listeners

946 Listeners
0 Listeners
16 Listeners

4 Listeners

524 Listeners

963 Listeners

426 Listeners

415 Listeners

823 Listeners

6,356 Listeners

346 Listeners

355 Listeners

483 Listeners

6,362 Listeners

112 Listeners

491 Listeners