
Sign up to save your podcasts
Or


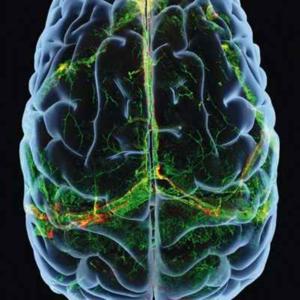

The scientific literature has shown that females demonstrate more aversion to risk-taking than males. Studies have also demonstrated that the basal lateral amygdala, or BLA, is a critical hub for processing risk and reward information. And yet further research has shown that activity in the amygdala differs between males and females, and that the expression of particular dopamine receptors called D2 receptors are greater in females than in males. The authors hypothesized that one mediating mechanism that leads to greater risk aversion in females is differential activity of dopamine in the basal lateral amygdala.
Caitlin Orsini is an assistant professor in the departments of psychology and neurology at UT Austin.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.
 View all episodes
View all episodes


 By Springer Nature
By Springer Nature




4
1515 ratings

The scientific literature has shown that females demonstrate more aversion to risk-taking than males. Studies have also demonstrated that the basal lateral amygdala, or BLA, is a critical hub for processing risk and reward information. And yet further research has shown that activity in the amygdala differs between males and females, and that the expression of particular dopamine receptors called D2 receptors are greater in females than in males. The authors hypothesized that one mediating mechanism that leads to greater risk aversion in females is differential activity of dopamine in the basal lateral amygdala.
Caitlin Orsini is an assistant professor in the departments of psychology and neurology at UT Austin.
Hosted on Acast. See acast.com/privacy for more information.

321 Listeners
2,057 Listeners

763 Listeners

125 Listeners

0 Listeners

4 Listeners

527 Listeners

961 Listeners

416 Listeners

822 Listeners

794 Listeners

354 Listeners

131 Listeners

9,192 Listeners

7,191 Listeners

253 Listeners

29,266 Listeners